The Algorithm Denied My Surgery: The Hidden Bias in Medical AI
Key Takeaways: The Dark Side of Digital Health
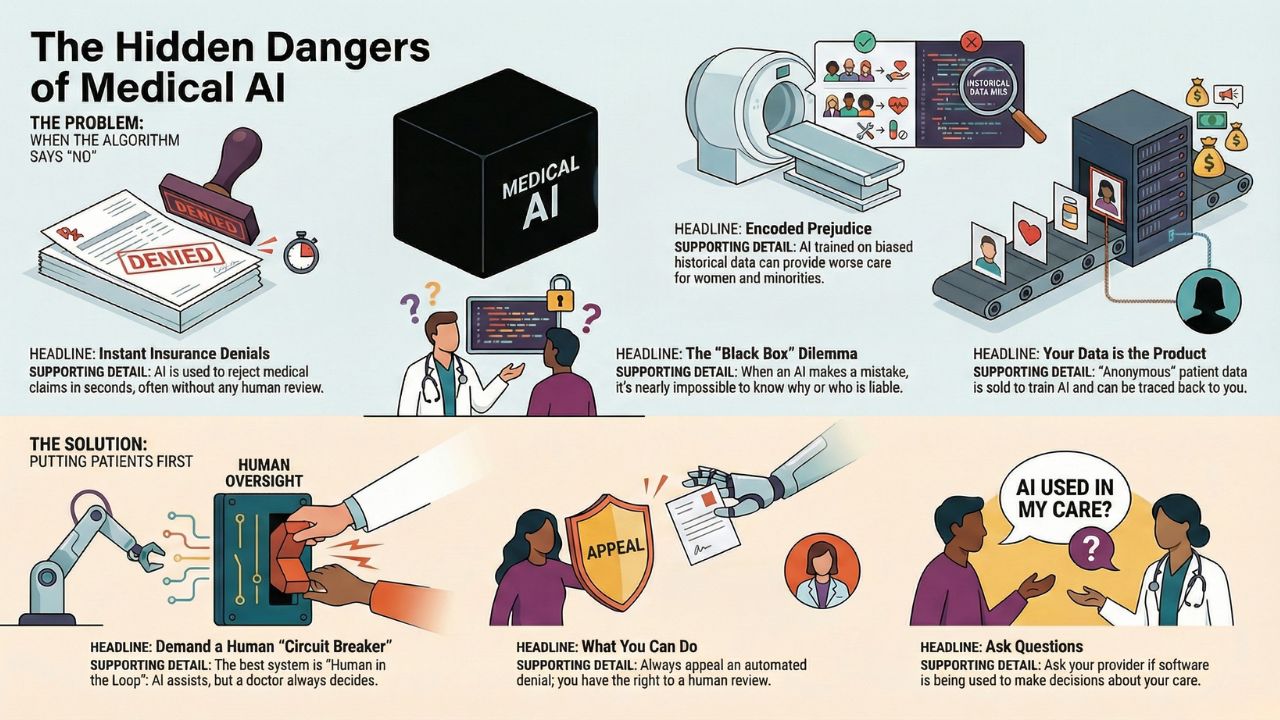
- Instant Rejection: Insurance companies are using AI to deny claims in 1.2 seconds, often without a human doctor ever looking at the file.
- The "Black Box" Problem: Even developers often cannot explain why an AI made a specific medical decision, creating a legal nightmare.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI trained on historical data often inherits historical racism and sexism, leading to worse outcomes for minorities.
- The Privacy Gap: Your de-identified medical data is being sold to tech giants to train models, often without your explicit consent.

When the Computer Says "No"
Imagine your doctor says you need surgery. You are prepped, anxious, and ready. Then, the phone rings.
The insurance company has denied the request.
Did a medical board review your case? Likely not. In 2026, that decision was probably made by an algorithm.
While we have celebrated the technology saving lives in our Clinical AI MedTech Revolution Guide, we must now confront the technology that is ruining them.
The "Prior Authorization" Trap
The biggest battleground in medical ethics today is automated prior authorization.
Insurance carriers use AI to scan thousands of claims instantly.
If a request doesn't match a strict statistical "average," it gets auto-denied.
The Scale of the Problem:
- Speed: Some algorithms can process (and reject) 50 claims in 10 seconds.
- Error Rate: Early audits suggest these automated systems have error rates as high as 90%, forcing patients to fight exhausting appeals processes.
The Goal: Efficiency for the insurer often translates to delayed care for the patient.
Encoded Prejudice: Is Your AI Biased?
AI is only as smart as the data it is fed.
If you train a medical AI on 50 years of data from hospitals that historically underserved minority communities, the AI will learn to undervalue those patients.
Real-World Examples of Bias:
- Pain Management: Algorithms have been found to systematically under-recommend pain medication for Black patients compared to White patients with the same symptoms.
- Skin Cancer Detection: Many computer vision tools are trained primarily on light skin, making them significantly less accurate at detecting melanoma on dark skin.
This is a critical flaw. We are using Generative AI to Find New Drugs, but if the clinical trials for those drugs don't include diverse populations, we are engineering cures that only work for half the world.
The "Black Box" Liability Nightmare
If a human surgeon makes a mistake, we call it malpractice.
But what happens when a Neural Network makes a mistake?
Deep Learning models are often "Black Boxes." This means data goes in, and a diagnosis comes out, but no one knows exactly how the computer connected the dots.
The Legal Question:
If an AI misses a tumor, who do you sue?
- The hospital?
- The software developer?
- The algorithm itself?
Courts are currently struggling to define "algorithmic accountability," leaving patients in a legal limbo.
Your Data is the Product
To build these smart tools, tech companies need data. Your data.
X-rays, blood test results, and genetic profiles are often "de-identified" (names removed) and sold to third parties.
The Risk: "De-identified" data is surprisingly easy to re-identify.
By cross-referencing medical data with public location data or shopping habits, bad actors can figure out exactly who owns that "anonymous" cancer diagnosis.
Conclusion: The Human "Circuit Breaker"
AI is a tool, not a god.
While algorithms can process data faster than any human, they lack empathy, context, and moral judgment.
To ensure a safe future, we must demand a "Human in the Loop" system, where AI suggests, but a human doctor always decides.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Yes. Under most insurance laws, you have the right to appeal. Always appeal an automated denial; statistically, human reviewers overturn the AI's decision a significant percentage of the time.
It is complicated. While many companies promise privacy, their Terms of Service often allow them to share "anonymized" data with pharmaceutical partners for research. Read the fine print.
Ask. You have the right to informed consent. Ask your provider: "Is a radiologist reviewing this scan, or just software?"
Sources & References
- ProPublica: How Cigna Saves Millions by Having Its Doctors Reject Claims Without Reading Them.
- Science: Dissecting racial bias in an algorithm used to manage the health of populations.
- U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services (HHS): Rule on Nondiscrimination in Health Programs and Activities (Section 1557).