The New HR: Hiring & Managing Your AI Agents
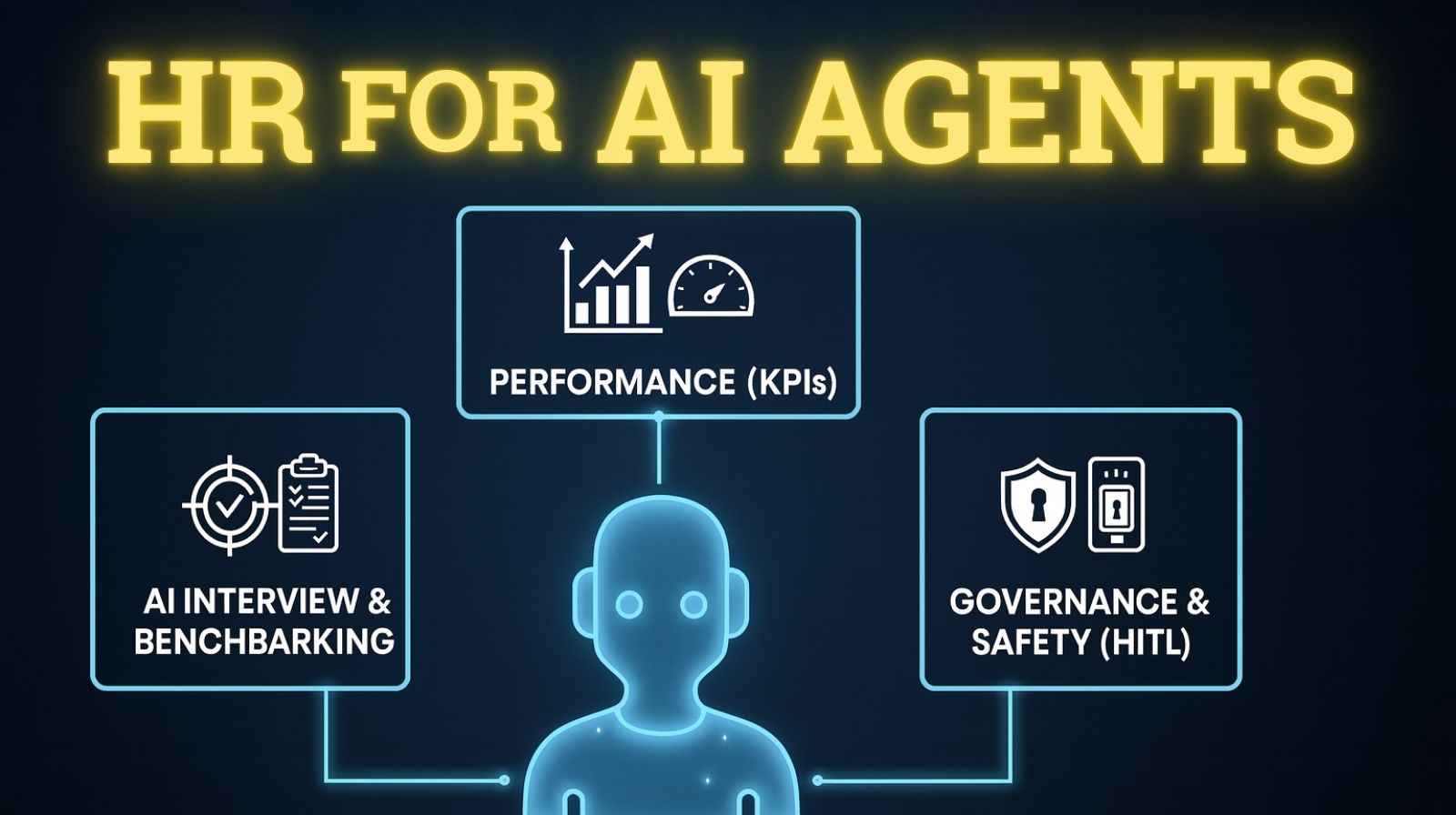
Imagine you don't just "install" a new piece of software; you "hire" a new team member. That's the profound shift happening right now in the world of smart technology. We're moving away from simple AI tools to sophisticated AI Agents, programs that can handle complex tasks and make decisions autonomously (on their own) to achieve a goal. As businesses worldwide adopt a forward-thinking AI Workforce Transformation Strategy 2026, they are realizing that managing these AI agents, our Digital Employees, requires the same care, structure, and accountability as managing human staff. To ensure they are safe, capable, and financially efficient, we need a complete, modern HR process designed specifically for effective AI Agent HR and Digital Employee Management. Here is the common-sense, three-step breakdown of how modern organizations hire, evaluate, and supervise their powerful new AI team members.
Related Deep Dives on the AI Workforce Transformation
Step 1: The AI Interview and Agent Benchmarking
You wouldn't hire a person without checking their skills and credentials. We must adopt the same rigorous approach for our AI agents, only digitally. This is the AI Recruitment Process.
Before an agent is allowed anywhere near a real customer or a critical company system, it must pass a structured evaluation called Agent Benchmarking. We call this the AI Interview.
- Results Over Resumes: Instead of reviewing a standard resume, we assess the agent's performance against clear, pre-defined metrics and goals. We make it prove its capabilities.
- Checking the Job Fit: This process is crucial to ensure the agent meets functional requirements. Can it truly handle the complexity of the job we hired it for? Can it process data accurately and quickly?
- Testing Under Pressure: This rigorous screening prevents us from deploying a poorly trained or unpredictable agent. It ensures quality and readiness from Day One, saving time and preventing costly mistakes before the agent ever impacts real business operations.
Step 2: The AI Agent Performance Review: Measuring True Value
Once successfully deployed, every AI agent is subject to a constant AI Agent Performance Review. This moves far beyond simple technical checks like "is the server running?". We need to measure the agent's actual value, productivity, and financial efficiency using specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
AI Autonomy Score
This is the ultimate measure of the agent's independence. It tracks how often the agent needs a person to step in, check its work, or give it instructions. A High Autonomy Score indicates the agent is self-sufficient and requires little to no human oversight. This is the essence of effective AI Hiring and Management, as it directly frees up human employees to focus on more creative and strategic tasks. A low score simply means the agent needs more training or human support.
Cost per Task / Token Burn
AI agents require computing resources (measured in "tokens") for every task. This KPI is all about financial efficiency. We carefully track the Cost per Task to ensure the agent isn't wasting valuable processing power. This keeps the operating budget predictable, confirming the AI is a smart investment.
Agent Error Rate
Accuracy is non-negotiable. This KPI measures how often the agent makes a mistake that is significant enough to require a human employee to correct it. A consistently Low Error Rate signifies a high-performing, trustworthy agent. This means less time spent by human staff fixing digital errors, greatly improving overall company efficiency and customer satisfaction.

Step 3: AI Governance: Safety, Accountability, and Control
This is the most critical element of Digital Employee Management. Since AI agents can act independently, we must build a strong framework for safety and accountability, called AI Governance. This is managed through clear protocols for human involvement.
The Human Loops: Our Supervision Strategy
We define exactly when and how humans interact with the AI to keep things safe:
- Human-on-the-Loop (HOTL): This is the strategic oversight team. The human reviews the agent's completed work. Their focus is on the big picture: ensuring compliance with laws, long-term strategy, and looking for unexpected trends.
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL): This is the active safety barrier. The human must intervene during a critical or high-risk task. For example, a HITL human must give the final sign-off if the agent is about to execute a major financial trade. This ensures immediate quality, safety, and accountability in real-time.
The Automated Emergency Stop: Circuit Breakers
No matter how well we train our agents, things can go wrong. What if an AI agent starts "hallucinating" (making up false information), violates a core company policy, or starts spending money far too quickly?
We install Circuit Breakers AI. These are automated "kill switches" or safety protocols that stop the agent immediately if it detects any dangerous activity. This acts as the ultimate safety net, ensuring the AI never goes rogue or causes significant, uncontrolled damage.
The future of business is digital, and the key to success is knowing how to manage your Digital Employees responsibly. By adopting an AI Agent HR system that treats AI like a valued, supervised team member, we ensure our new workforce is not only incredibly powerful but also safe, compliant, and cost-effective for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An AI Agent (or Digital Employee) is an advanced software program that can act and make decisions autonomously (on its own) to achieve a complex goal. Unlike simple software that just follows a fixed script, an AI Agent can reason, plan, use various tools, and adapt its actions with minimal human input, just like a human employee.
Because AI Agents have autonomy and can access critical systems, they pose higher risks if they make a mistake or "hallucinate." Treating the process like a "hiring" ensures you formally vet their skills (Benchmarking), set performance goals (KPIs), and put safety rules (Governance) in place before they start working.
The difference between HITL and HOTL relates to the timing and nature of human involvement in AI processes. HITL, or Human-in-the-Loop, is used during a critical task or decision. In this role, the human acts as an Active Approver or intervenor, which ensures immediate safety. Conversely, HOTL, or Human-on-the-Loop, is used after the task is completed. The human's role in HOTL is that of a Strategic Monitor, reviewing the finished work for compliance and long-term improvements.
Circuit Breakers are automated "kill switches" or safety protocols. If an AI Agent starts exhibiting dangerous behaviour, such as violating a data privacy rule, making costly mistakes, or generating false information (hallucinating), the circuit breaker instantly stops the agent, preventing immediate and potentially severe damage.