New AI Strategy: Meet the Prompt Architect and Agent Orchestrator
The AI Workforce Transformation is not merely an upgrade; it’s a complete re-architecture of how businesses operate.
The power in the Future of Work is no longer held solely by the traditional coder, but by a new class of leaders who design the very intent and manage the complex teamwork of autonomous systems. This technological shift is heralded by the rise of the AI Agent, a sophisticated digital worker capable of autonomously completing complex, multi-step tasks. The demand for a cohesive, scalable AI Strategy has created two incredibly crucial, high-impact specializations for 2026 and beyond: The Prompt Architect and the Agent Orchestrator.
Related Deep Dives on the AI Workforce Transformation
The Prompt Architect: Designing the AI's "Digital Soul"
The Prompt Architect is arguably the most paramount role in the new AI ecosystem. Think of them as the Chief Personality Officer or the lead writer for your AI. They aren't simply engineers typing clever inputs; they are creating the foundational character, the essential ethical guardrails, and the core operational purpose of every AI Agent in your company.
What the Prompt Architect Really Does?
This role centers on the mastery of Prompt Engineering, specifically by crafting the essential System Prompts. A System Prompt is the deep, meta-instruction, the hidden blueprint that tells the Large Language Model (LLM) who it is, what its boundaries are, and how it must behave before any user even interacts with it. By perfecting this foundational layer, the Prompt Architect ensures topical relevance and maximizes alignment between the AI’s output and the overall business goals.
Key elements a Prompt Architect designs into the System Prompts include:
- Context & Persona: Defining the AI's role (e.g., "You are a customer support agent with 10 years of experience") and its tone (e.g., "Always be empathetic and concise").
- Policies & Guidelines: Establishing non-negotiable rules, such as safety policies or operational constraints (e.g., "Never guess or hallucinate, always cite a verifiable source").
- Tool Workflow: Instructing the AI Agent on the exact conditions and parameters for when it should use an external tool, like a search API or an internal database.
| Role | Analogy | The Core Task | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt Architect | The Screenwriter and Ethicist | "Crafts the System Prompt (the deep, meta-instruction)" | "Language, Ethics, Persona, Aligning AI purpose with business strategy" |
Why This Role is Paramount: From Persona to Policy
Enforcing Behavior (The Persona): This is the heart of the role. If your crucial "Resolution Agent" is required to act with a specific, friendly, and patient way across thousands of high-stakes customer chats, it’s the Prompt Architect who writes the digital DNA, the System Prompts, to enforce that behaviour consistently. They turn soft skills into hard code.
Setting Ethical and Operational Boundaries: They are the first line of defense in AI Governance. They install the ethical constraints and operational "red lines," ensuring the AI doesn't stray into prohibited topics, share confidential data, or generate biased outputs. This requires a deep understanding of compliance, not just code.
Shifting Focus from Code to Language: The success of modern AI is dictated by the quality of instructions, not the size of the model. This role is about translating complex business needs, user experience requirements, and legal policies into simple, yet incredibly effective "System Prompts" that guide the agent's every decision and response. The power is in the precision of the language.
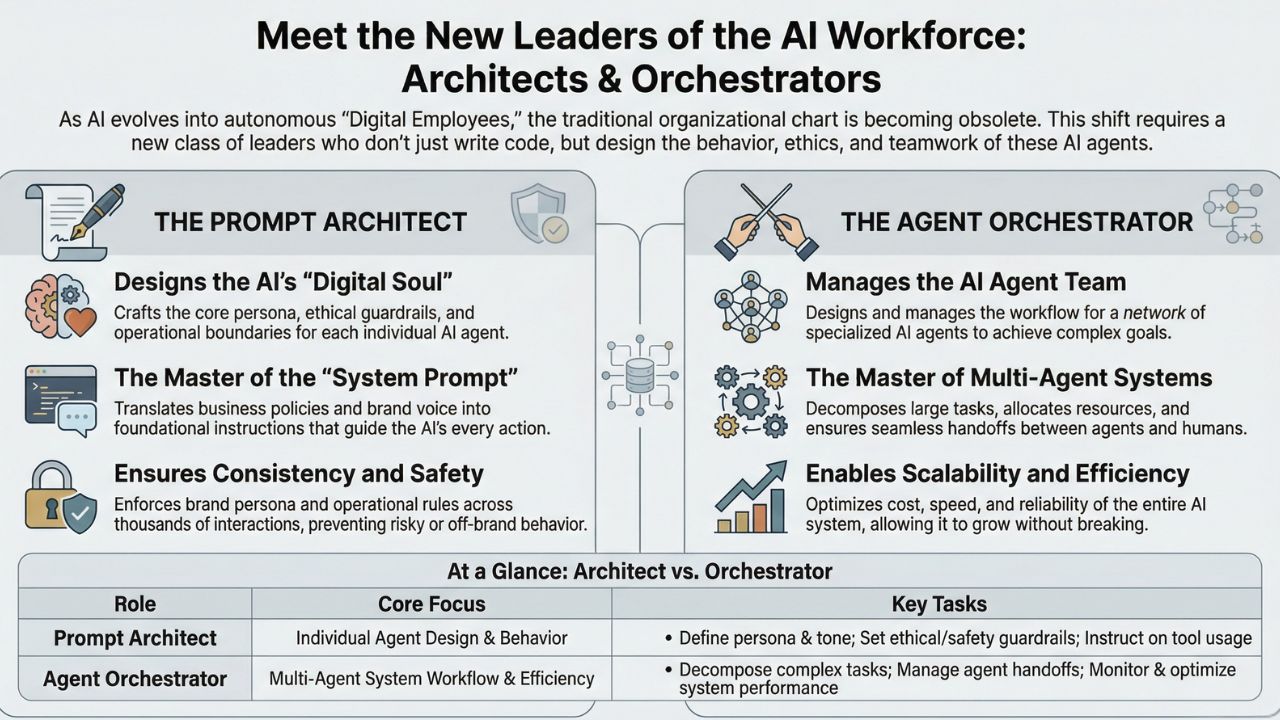
The Agent Orchestrator: The Conductor of the Multi-Agent System
If the Prompt Architect designs the mind of a single AI Agent, the Agent Orchestrator manages the entire autonomous digital team. This role is the digital project manager, the conductor who turns a collection of powerful individual agents into a cohesive, high-performing Multi-Agent System. A single AI Agent might be great at writing a first draft, but a complex business process, like processing a claim or managing a global supply chain, requires a team. This is where the Agent Orchestrator steps in, coordinating a network of specialized agents to achieve a single, complex goal.
Core Responsibilities in Multi-Agent Systems
The primary value proposition of the Agent Orchestrator is system-level optimization. They manage the overall system's cost, speed, and resource allocation across multiple specialized agents. Their responsibilities include:
- Task Decomposition: Breaking down a huge, ambiguous goal (e.g., "Develop next quarter's marketing strategy") into smaller, manageable sub-tasks that individual agents can handle (e.g., "Analyze Q3 sales data," "Draft social media copy," "Generate visual assets").
- Resource Allocation: Determining which specialized AI Agent or external tool (like a CRM or a data analysis platform) is best suited for each sub-task in real-time.
- Dependency Management: Ensuring the correct sequence and seamless "handoff" of data between agents (e.g., the "Data Analysis Agent" must finish before the "Report Generation Agent" can start).
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously tracking the Multi-Agent System’s performance to identify bottlenecks and refine the workflow.
| Role | Analogy | The Core Task | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent Orchestrator | The Conductor and Project Manager | "Designs and manages multi-step workflows, ensuring Agents communicate flawlessly, correctly pass data between specialties, and manage structured handoffs to human experts." | "Ensuring seamless, efficient end-to-end task completion" |
Why They Are the New Workflow Manager: Managing the Team Flow
Seamless Hand-Offs and Data Integrity: The Orchestrator ensures that the "Research Agent" finishes its data collection phase and passes the exact correct, validated data format to the "Writing Agent," which then feeds the "Presentation Agent." This prevents friction, eliminates lost context, and guarantees reliable output across the chain.
Tackling Hierarchical Complexity (Triage): Their job often involves managing complex, tiered systems. For instance, they design the flow where a "Triage Agent" analyzes an incoming request, decides if it's simple enough for an automated response, or complex enough to be routed to a "Human Specialist" with full context attached.
Scalability and Resilience: When the business needs to rapidly scale its AI capabilities, say, adding a new language agent or integrating a new regulatory compliance check, the Agent Orchestrator is the one who plugs the new specialized agents into the existing flow without causing any systemic breakdown. They ensure the entire multi-agent system remains fast, reliable, and compliant, making them essential for sustainable growth.
The Shift from Technical Skill to Strategic Design
The most important insight for AI Workforce Transformation Strategy 2026 is crystal clear: The bottleneck of AI adoption is no longer technology itself, it’s human design, ethical management, and strategic oversight. As AI Agents take over more of the rote coding and repetitive tasks, the most valuable employees will be those who can think critically and strategically about language, ethics, and system flow. They are the new architects of digital value. These new roles, The Architects and The Orchestrators, are not just managerial positions; they are the strategic translators who build the structure, define the values, and ultimately, lead your company into the next era of high-efficiency, responsible, and scalable AI-powered work.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No, not primarily. While they need a technical understanding of how Large Language Models (LLMs) process information, the role is less about writing traditional code (like Python or Java) and more about language design, ethics, and psychology. The Prompt Architect uses highly specialized instructions, called System Prompts, to influence the AI's core behaviour, tone, and operational rules, functioning more like a behavioural designer than a coder.
The System Prompt is a hidden set of top-level instructions given to an AI Agent before any user input. It acts as the agent’s “digital DNA” by defining its role, tone, and ethical limits, for example, telling it to behave as a patient customer service representative, respond with empathy, and avoid giving legal or financial advice. These instructions ensure the agent stays consistent across all interactions.
The Agent Orchestrator works with tools built specifically for multi-agent systems and workflow automation. They use orchestration frameworks like LangGraph, CrewAI, and AutoGen to design complex, conditional workflows for AI agents. They also use low-code or no-code platforms such as Flowise and n8n, which provide easy drag-and-drop interfaces for connecting AI services and APIs. In addition, they rely on Agent-to-Agent (A2A) protocols that ensure secure, structured communication between different agents, even when those agents run on different platforms.
Autonomy requires governance, and these roles ensure it stays safe and aligned with business goals. The Architect maintains alignment by ensuring the AI follows brand voice, policies, and ethical guidelines. Both the Architect and Orchestrator handle safety by setting guardrails and defining human-in-the-loop checkpoints, with the Orchestrator managing when tasks should pause or escalate to a human. The Orchestrator also ensures efficiency by optimizing cost, speed, and resources across multiple agents.
Sources and References
- 1. AI Workforce Transformation Strategy 2026
- 2. Gartner Survey Finds AI Will Touch All IT Work by 2030
- 3. Agents, robots, and us: Skill partnerships in the age of AI
- 4. Gartner Predicts Agentic AI Will Autonomously Resolve 80% of Common Customer Service Issues Without Human Intervention by 2029
- 5. Effective context engineering for AI agents
- 6. AI Ethics and Governance for Organisational Agility
- 7. OpenAI: A practical guide to building agents
- 8. We Tested 14 AI Agent Frameworks. Here's How to Choose.
- 9. What is A2A protocol (Agent2Agent)?